Artificial Intelligence: The 21st Century Technological Revolution
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science that focuses on developing systems that mimic human cognitive abilities such as thinking, learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. AI has become a major topic in global discussions on the future of technology due to its immense potential to revolutionize various aspects of life, from healthcare and industry to entertainment.
With rapid advancements in computing power, algorithms, and big data, AI is no longer a futuristic concept but an integral part of everyday life. This article provides an in-depth overview of AI, its historical development, various types, its applications across sectors, and the challenges it poses.
Definition and Brief History of AI
What is AI?
AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. These processes include learning (acquiring information and rules), reasoning (using rules to reach conclusions), and self-correction. AI systems can be software or hardware designed to perform specific tasks automatically, often more efficiently than humans.
A Brief History of AI
-
1950s: British computer scientist Alan Turing popularized the idea of machine intelligence in his seminal paper “Computing Machinery and Intelligence”, posing the question, “Can machines think?”
-
1956: The term “Artificial Intelligence” was officially introduced at the Dartmouth Conference led by John McCarthy. This marked the birth of AI as a distinct academic discipline.
-
1970s–1980s: The development of expert systems, software programs that mimic the decision-making ability of human experts.
-
2000–Present: Advancements in big data, machine learning, and computing power have led to more sophisticated and widespread AI applications.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
AI is categorized based on its capabilities:
-
Narrow AI (ANI – Artificial Narrow Intelligence)
Focuses on specific tasks like facial recognition, internet searches, or recommendation algorithms (e.g., Netflix). -
General AI (AGI – Artificial General Intelligence)
Possesses intellectual capabilities comparable to humans. AGI can learn, understand, and perform any cognitive task. It is still under development and represents a long-term goal of AI research. -
Superintelligent AI (ASI – Artificial Superintelligence)
Surpasses human intelligence in all areas, including creativity, decision-making, and social skills. Experts like Stephen Hawking and Elon Musk have warned about the risks of ASI if not properly controlled.
Supporting Technologies and Concepts
-
Machine Learning (ML)
A subset of AI that enables machines to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. Common in fraud detection and email spam filtering. -
Deep Learning
A subfield of ML using neural networks inspired by the human brain. It’s highly effective in speech and image recognition. -
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Allows machines to understand and respond to human language. Used in chatbots, auto-translators, and virtual assistants. -
Computer Vision
Enables computers to “see” and identify objects in images or videos. Key areas in autonomous vehicles, security, and medical imaging.
Applications of AI in Various Fields
-
Healthcare
AI revolutionizes healthcare with automated diagnosis, medical image analysis, and disease prediction. For example, AI can detect cancer early via X-ray or MRI scans. Health chatbots offer preliminary consultations before seeing a doctor. -
Education
Adaptive learning systems adjust material to each student’s pace and style. AI also automates grading and provides quick feedback. -
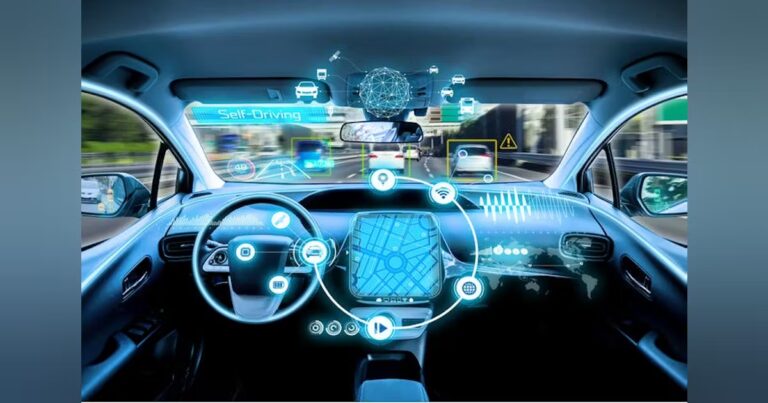
Transportation and Autonomous Vehicles
Companies like Tesla and Waymo use AI to power self-driving cars using sensors, cameras, and algorithms to detect traffic signals, pedestrians, and other vehicles. -
Finance
AI is used in risk analysis, asset management, and fraud detection. Banking chatbots assist customers with financial services. -
Industry and Automation
AI-driven robots streamline production lines and predictive maintenance forecasts equipment failure before it happens. -
Entertainment and Media
Platforms like YouTube and Spotify use AI to recommend content. Deepfake and generative AI technologies create highly realistic visual and audio content.
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence
-
Efficiency: Performs tasks rapidly and tirelessly.
-
High Accuracy: Excels in fields like data analysis and medical diagnostics.
-
Cost-Effective: Reduces long-term operational costs through automation.
-
Customization: AI services can be tailored to individual preferences.
-
Better Decision Making: Analyzes large datasets swiftly to support strategic decisions.
Challenges and Risks of AI
-
Job Displacement
Automation may replace human workers, especially in manufacturing, transport, and customer service, leading to economic and social concerns. -
Ethics and Privacy
AI in surveillance and personal data analysis raises concerns over privacy and freedom. Ethical boundaries must be established. -
Bias and Discrimination
AI systems trained on biased data can produce biased outcomes. For example, recruitment algorithms that discriminate based on gender or race. -
Overdependence
Overreliance on AI might diminish human critical thinking and initiative. -
Security Threats
AI can be misused for cyberattacks, creating fake content (deepfakes), or building autonomous weapons.
The Future of Artificial Intelligence
The future of AI is promising yet challenging. Key directions include:
-
Ethical and Transparent AI
Research is focused on explainable AI, making systems accountable and trustworthy. -
Human-Machine Collaboration
Emphasis on augmented intelligence, where AI supports human productivity rather than replaces it. -
AI in Developing Countries
Offers affordable solutions for healthcare, education, and agriculture in under-resourced areas. -
Global Regulation and Policy
Calls for international legal frameworks to ensure fair and safe AI development and use.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence stands as a cornerstone of the 21st-century digital revolution. With its vast potential to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and quality of life, AI brings immense value across industries. However, it also introduces ethical, social, and economic challenges that must be addressed wisely.
The future of AI will depend on how responsibly we develop it today—whether to empower or diminish humanity. Therefore, governments, scientists, businesses, and society need to collaborate in ensuring AI becomes a force for good.





